What Does A Er Do In A Animal Cell
Quick await
Rough ER (RER) is involved in some poly peptide production, protein folding, quality control and despatch. It is called 'rough' because it is studded with ribosomes
Polish Eastward R (SER) is associated with the product and metabolism of fats and steroid hormones. It is 'smoothen' because it is not studded with ribosomes and is associated with smooth slippery fats.
To view a micrograph of ER interpreted using the Gridpoint cross-hairs device, click here.
CELLS Demand THE Rough AND THE Shine
Think of a cell as a "multitude of membranes" we said in an earlier section. This statement certainly applies to the endoplasmic reticulum an organelle found in eukaryotic cells.
Almost fifty% of the total membrane surface in an animal prison cell is provided by endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The organelle chosen 'endoplasmic reticulum' occurs in both plants and animals and is a very important manufacturing site for lipids (fats) and many proteins. Many of these products are made for and exported to other organelles.
-
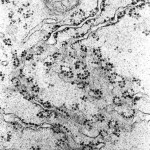
This is an electron microscope prototype showing role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum in a plant root cell from maize. The dark spots are ribosomes.
(courtesy of Chris Hawes, The Inquiry School of Biology & Molecular Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, Britain)
In that location are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) and smoothen endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER). Both types are nowadays in establish and animal cells. The two types of ER often appear equally if carve up, but they are sub-compartments of the same organelle. Cells specialising in the production of proteins will tend to have a larger amount of crude ER whilst cells producing lipids (fats) and steroid hormones will have a greater corporeality of shine ER.
Part of the ER is face-to-face with the nuclear envelope. The Golgi apparatus is as well closely associated with the ER and contempo observations propose that parts of the ii organelles, i.e. the ER and the Golgi circuitous, are so close that some chemical products probably laissez passer directly betwixt them instead of beingness packaged into vesicles (droplets enclosed within a membrane) and transported to them through the cytoplasm
ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
This is an extensive organelle composed of profoundly convoluted only flattish sealed sacs, which are contiguous with the nuclear membrane. It is called 'rough' endoplasmic reticulum because it is studded on its outer surface (the surface in contact with the cytosol) with ribosomes. These are called membrane jump ribosomes and are firmly fastened to the outer cytosolic side of the ER Virtually 13 1000000 ribosomes are nowadays on the RER in the average liver jail cell. Rough ER is found throughout the jail cell but the density is higher virtually the nucleus and the Golgi apparatus.
Ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum are called 'membrane bound' and are responsible for the assembly of many proteins. This process is called translation. Certain cells of the pancreas and digestive tract produce a high book of protein as enzymes. Many of the proteins are produced in quantity in the cells of the pancreas and the digestive tract and function as digestive enzymes.
The rough ER working with membrane bound ribosomes takes polypeptides and amino acids from the cytosol and continues protein assembly including, at an early stage, recognising a 'destination label' attached to each of them. Proteins are produced for the plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicles, plant vacuoles, lysosomes, endosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum itself. Some of the proteins are delivered into the lumen or space inside the ER whilst others are candy within the ER membrane itself. In the lumen some proteins have sugar groups added to them to class glycoproteins. Some have metal groups added to them. It is in the rough ER for case that four polypeptide chains are brought together to course haemoglobin.
Protein folding unit
Information technology is in the lumen of the crude ER that proteins are folded to produce the highly important biochemical architecture which volition provide 'lock and key' and other recognition and linking sites.
Protein quality control section
It is also in the lumen that an amazing process of quality control checking is carried out. Proteins are subjected to a quality control check and any that are found to be incorrectly formed or incorrectly folded are rejected. These rejects are stored in the lumen or sent for recycling for eventual breakdown to amino acids. A type of emphysema (a lung problem) is caused by the ER quality control section continually rejecting an incorrectly folded protein. The protein is wrongly folded as a result of receiving an contradistinct genetic message. The required protein is never exported from the lumen of crude ER. Research into poly peptide structure failures relating to HIV are also focusing on reactions in the ER.
Rigorous quality control plays a role in cystic fibrosis
A form of cystic fibrosis is caused by a missing unmarried amino acrid, phenylanaline, in a particular position in the protein construction. The protein might work well without the amino acid but the very exacting service provided by the quality control department spots the fault and rejects the protein retaining it in the lumen of the rough ER. In this case the customer (the person with cystic fibrosis) loses out completely due to high standards when a slightly poorer production would have been improve than no production at all.
From Rough ER to Golgi
In almost cases proteins are transferred to the Golgi appliance for 'finishing'. They are conveyed in vesicles or perhaps directly between the ER and Golgi surfaces. After 'finishing' they are delivered to specific locations.
SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Shine ER is more tubular than crude ER and forms an interconnecting network sub-compartment of ER. It is plant fairly evenly distributed throughout the cytoplasm.
It is non studded with ribosomes hence 'smooth' ER.
Smooth ER is devoted about exclusively to the manufacture of lipids and in some cases to the metabolism of them and associated products. In liver cells for example polish ER enables glycogen that is stored as granules on the external surface of smooth ER to be broken downwardly to glucose. Smooth ER is besides involved in the production of steroid hormones in the adrenal cortex and endocrine glands.
Polish ER – the detox stop
Smooth ER besides plays a large office in detoxifying a number of organic chemicals converting them to safer water-soluble products.
Large amounts of smooth ER are constitute in liver cells where ane of its main functions is to detoxify products of natural metabolism and to try to detoxify overloads of ethanol derived from excess alcoholic drinking and also barbiturates from drug overdose. To aid with this, smooth ER tin can double its surface area within a few days, returning to its normal size when the assault has subsided.
The contraction of muscle cells is triggered by the orderly release of calcium ions. These ions are released from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
SUMMARY
-
Endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle found in both eukaryotic animal and plant cells. It oftentimes appears as ii interconnected sub-compartments, namely rough ER and smooth ER. Both types consist of membrane enclosed, interconnected flattened tubes.
-
The rough ER, studded with millions of membrane spring ribosomes, is involved with the production, folding, quality control and despatch of some proteins.
-
Smooth ER is largely associated with lipid (fatty) manufacture and metabolism and steroid product hormone production. It also has a detoxification function.
Amended 19.11.xv DA.
Source: https://bscb.org/learning-resources/softcell-e-learning/endoplasmic-reticulum-rough-and-smooth/
Posted by: morristhoures.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Does A Er Do In A Animal Cell"
Post a Comment